Remembering the stages of mitosis can be a challenge, especially when studying cell division. But fret not! We have a memory aid that will make it easier for you to recall the intricate process of mitosis. Mnemonic techniques offer a creative and effective approach to memorizing complex concepts. In this article, we will explore various mnemonic devices and patterns that will help you remember the steps of mitosis.
Cell division is a fundamental part of the cell cycle, consisting of four main phases: G1, S phase, G2, and mitosis. Mitosis, also known as meiosis, is the stage where the actual cell division occurs. To better understand the stages of mitosis, it’s crucial to have a clear grasp of the cell cycle and its different phases. External growth factors play a role in stimulating cells to progress through the cycle, and the restriction point in G1 marks a point of no return.
Key Takeaways:
- Mnemonic techniques can help in remembering the stages of mitosis
- Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle, consisting of G1, S phase, G2, and mitosis itself
- External growth factors trigger cells to progress through the cell cycle
- The restriction point in G1 marks a turning point in a cell’s response to growth factors
- Mitosis involves interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis
Table of Contents
Understanding the Cell Cycle
The cell cycle is a crucial process that allows cells to grow, replicate their DNA, and divide. It consists of two main stages: interphase and the mitotic phase (M phase). Let’s explore the different phases of the cell cycle in more detail:
G1 Phase (Gap 1)
The G1 phase is the first stage of interphase and stands for Gap 1. During this phase, cells grow in size and synthesize proteins. They also carry out their normal functions and prepare for DNA replication. G1 is a crucial checkpoint where the cell assesses its environment and decides whether to continue with the cell cycle or enter a resting state called G0.
S Phase (Synthesis)
The S phase is the second stage of interphase and stands for Synthesis. During this phase, DNA replication takes place. The genetic material is duplicated to ensure that each daughter cell receives an exact copy of the parent cell’s DNA. This replication process is essential for cell division to occur accurately.
G2 Phase (Gap 2)
The G2 phase is the final stage of interphase, which stands for Gap 2. During this phase, the cell prepares for mitosis or cell division. The cell continues to grow, synthesize proteins, and produce organelles necessary for cell division. G2 is another crucial checkpoint where the cell checks for DNA damage before proceeding to mitosis.
The cell cycle is a highly regulated process that ensures the proper growth and division of cells. Understanding the different phases of the cell cycle, including G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phase, provides insights into the intricate mechanisms that govern cell division.
The Process of Mitosis
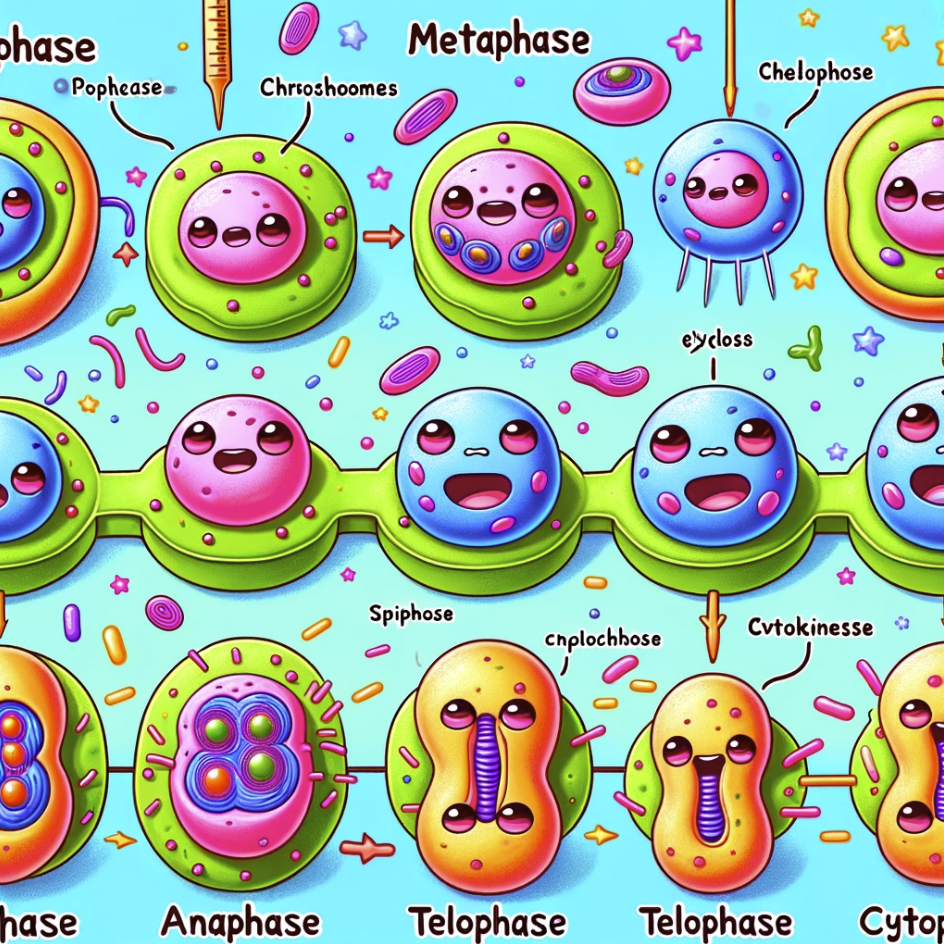
Mitosis is a crucial process of cell division that allows for growth, repair, and the creation of new cells. It is a highly orchestrated series of events that can be divided into several distinct stages. Let’s explore the stages of mitosis in detail:
Interphase
Interphase is the initial phase of the cell cycle, comprising three stages: G1, S, and G2. During G1, the cell grows and synthesizes proteins. S phase is when DNA replication occurs, resulting in the duplication of the cell’s genetic material. In G2, the cell prepares for mitosis by synthesizing the necessary proteins.
Prophase
In prophase, the chromatin material within the nucleus begins to condense into dense, visible structures called chromosomes. Each chromosome consists of two identical sister chromatids held together at a region called the centromere. The nuclear envelope starts to break down, and the spindle apparatus begins to form.
Metaphase
During metaphase, the spindle apparatus aligns the chromosomes along the equator of the cell. This alignment ensures that each daughter cell receives an equal number of chromosomes during division.
Anaphase
Anaphase is a dynamic stage where the sister chromatids separate at the centromere and are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell. This process ensures that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes.
Telophase
Telophase is characterized by the reformation of the nuclear envelope around each set of daughter chromosomes. The chromosomes begin to decondense, and the spindle apparatus disassembles. Cell division is now imminent.
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is the final stage of mitosis and involves the physical separation of the cytoplasm into two daughter cells. In animal cells, a contractile ring of actin filaments forms along the equator of the cell, which contracts and pinches the cell membrane to divide the cytoplasm. In plant cells, a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Interphase | The cell grows and replicates its DNA. |
| Prophase | The chromatin condenses, and the nuclear envelope breaks down. |
| Metaphase | The chromosomes align along the equator of the cell. |
| Anaphase | The sister chromatids separate and move towards opposite poles. |
| Telophase | The nuclear envelope reforms, and the cell prepares for division. |
| Cytokinesis | The cytoplasm divides, resulting in two daughter cells. |
Mnemonic Techniques for Mitosis
When it comes to remembering the stages of mitosis, mnemonic techniques can be a helpful tool. Mnemonics are memory aids that use creative and memorable methods to facilitate learning and recall. Here are some mnemonic devices that can make the process of memorizing the stages of mitosis easier and more enjoyable:
Imagery Mnemonics
Imagery mnemonics involve creating visual images or mental pictures that are associated with each stage of mitosis. For example, you can imagine the chromosomes aligning on the “Metaphase Merry-Go-Round” or the chromatids separating like a “Telephoning Sister”. These vivid mental images can help you remember the sequence and characteristics of each stage.
Acronyms and Acrostics
Acronyms and acrostics are mnemonic techniques that use the first letters of each stage to create a word or sentence. For instance, you can create the acronym “IPMATC” to represent the stages of Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, and Cytokinesis. Alternatively, you can use acrostics to form a memorable phrase. For example, “I Prevail, My Aunt Talks Cheerfully” can help you recall the stages in order.
Rhymes
Using rhymes is another effective mnemonic technique for memorizing the stages of mitosis. You can create rhymes or catchy phrases that highlight the key aspects of each stage. For example, “Prophase begins, chromosomes condense” or “Anaphase, chromatids breakaway”. The rhythm and rhyme of these phrases can make the information stick in your mind.
Chunking
Chunking involves grouping the stages of mitosis into meaningful clusters based on their similarities or characteristics. For example, you can group Interphase, Prophase, and Metaphase as the “Preparation Phase” because they involve the initial preparation and alignment of the chromosomes. Similarly, Anaphase and Telophase can be grouped as the “Division Phase” because they involve the separation and formation of new nuclei. By chunking the stages, you can simplify the information and make it easier to remember.
These mnemonic techniques offer creative and engaging ways to remember the stages of mitosis. Whether you prefer visual imagery, acronyms, rhymes, or chunking, finding a mnemonic method that resonates with you can greatly enhance your memory and understanding of cell division. So why not give these techniques a try and make mitosis a memorable journey!
The Power of Mnemonics on the MCAT
Mnemonics can be a powerful tool for studying and memorizing high-yield topics on the MCAT. By using mnemonic techniques, students can create correlations among facts, making it easier to remember and recall them. These techniques have been shown to enhance learning, retention, and performance in recall exams.
While mnemonic strategies are helpful, it’s important to use them in conjunction with understanding and contextualizing the material. The MCAT covers a wide range of topics, and mnemonic techniques can assist students in organizing and recalling the information effectively. By applying mnemonic devices, such as acronyms, acrostics, imagery, rhymes, and chunking, students can enhance their memory recall and improve their overall performance on the MCAT.
For example, imagine using an acronym like “PMATC” to remember the stages of mitosis: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis. This simple mnemonic can serve as a mental framework for recalling the sequence of events during cell division.
Additionally, visual imagery can play a significant role in memorizing complex topics. Creating mental images that represent specific concepts can aid in their retention and recall. For instance, visualizing chromosomes lined up like soldiers on a battlefield during metaphase can help reinforce the understanding of this stage of mitosis.
“Mnemonic techniques on the MCAT have been shown to enhance learning, retention, and performance in recall exams.”
However, it’s important to note that mnemonic strategies should not replace a thorough understanding of the material. They are most effective when used alongside comprehension and critical thinking. Understanding the underlying concepts and connecting them to mnemonic devices can foster a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Ultimately, by harnessing the power of mnemonics, students can improve their memory recall, master high-yield topics, and confidently tackle the MCAT exam.
| Mnemonic Technique | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Acronyms and Acrostics | Create memorable words or sentences using the first letters of each stage or concept |
| Imagery Mnemonics | Associate mental images with specific information to aid in recall |
| Rhymes | Create memorable phrases or rhymes to remember key facts or sequences |
| Chunking | Group information into meaningful chunks to make it more manageable |
Recommended Resources
- Memorable Mnemonics for the MCAT – A comprehensive guidebook that provides a wide range of mnemonic techniques specifically tailored for the MCAT.
- The Art of Memory: Techniques for Effective Memorization – A book that explores various mnemonic strategies and how they can be applied to improve memory recall.
- MCAT Prep Mnemonics Course – An online course that focuses on teaching effective mnemonic techniques for the MCAT, helping students memorize high-yield topics with ease.
Different Types of Mnemonics
When it comes to aiding memory recall, there are various types of mnemonic techniques that can be utilized. These techniques help individuals associate information with different mental strategies, making it easier to remember and retain. Here are some popular types of mnemonics:
1. Imagery Mnemonics
Imagery mnemonics involve creating vivid mental pictures or visualizations associated with the information you want to remember. By linking new information to familiar or striking images, your brain can recall the associated visuals, leading to improved memory retrieval.
2. Acronyms and Acrostics
Acronyms and acrostics provide a way of creating memorable word patterns by using the first letters of words or sentences. By forming an acronym or an acrostic using the initial letters of the items to be remembered, you can create a catchy and easily recallable phrase.
3. Rhymes
Rhymes are an effective mnemonic technique that uses rhythm and rhyming patterns to enhance memory. By incorporating rhymes into the information you want to remember, you create a catchy phrase that triggers better recall. The rhythmic and melodic qualities of rhymes aid in the encoding and retrieval of information.
4. Chunking
Chunking involves breaking down large amounts of information into smaller, more manageable chunks. By organizing related pieces of information into groups, your brain can process and remember them more effectively. Chunking allows you to focus on the main ideas or themes, making it easier to mentally grasp and recall the information.
Each type of mnemonic technique offers its unique advantages and can be employed based on personal preference and the nature of the information being learned. Experiment with different techniques to discover which ones work best for you and help enhance your memory recall.
Conclusion
Mnemonic techniques are a powerful tool for students studying complex topics like mitosis. By using mnemonic devices, students can make the process of memorization more enjoyable and effective. Instead of relying solely on rote memorization, mnemonics provide a creative and engaging way to remember key details and concepts.
While mnemonics can be incredibly helpful, it’s important to remember that they should be used in conjunction with other study techniques and a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter. A well-rounded study plan that incorporates mnemonic techniques, active learning strategies, and regular review will yield the best results.
For students preparing for the MCAT, mnemonic techniques can be particularly beneficial in remembering high-yield topics. The MCAT covers a wide range of complex scientific concepts, and mnemonic techniques can help students organize and recall this information effectively. By using mnemonic strategies and creating personalized memory aids, students can master mitosis and other important concepts on the MCAT.
In conclusion, mnemonic techniques offer a valuable approach to enhance memory and understanding. Whether you’re studying mitosis or preparing for the MCAT, incorporating mnemonic devices into your study routine can greatly improve your learning experience. With the right memory techniques and a comprehensive study plan, you can boost your retention and excel in your academic pursuits.
FAQ
What is the cell cycle?
The cell cycle is the series of events that takes place in a cell that results in DNA replication and cell division. It consists of two main stages: interphase and the mitotic phase (M phase).
What are the phases of the cell cycle?
The phases of the cell cycle are G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phase. During G1 phase, cells grow and synthesize proteins. S phase is when DNA replication occurs. G2 phase is the stage before mitosis where the cell prepares for cell division.
What is mitosis?
Mitosis is the process of cell division and is one of the stages of the cell cycle. It consists of several stages, including interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis.
What happens during interphase?
Interphase is the stage before mitosis. During interphase, the cell grows, replicates its DNA, and prepares for cell division.
What happens during prophase?
Prophase is when the chromatin material shortens and thickens into individual chromosomes. The nuclear membrane also begins to dissolve.
What happens during metaphase?
Metaphase is when the chromosomes line up on the equator of the cell. This alignment ensures that each daughter cell will receive the correct number of chromosomes during cell division.
What happens during anaphase?
Anaphase is when the chromatids, which make up each chromosome, are pulled to opposite poles of the cell by spindle fibers.
What happens during telophase?
Telophase is when the nuclear membrane reforms around the daughter chromosomes at each pole of the cell. The chromosomes begin to unwind back into chromatin.
What is cytokinesis?
Cytokinesis is the process of the cytoplasm splitting into two, resulting in the formation of two daughter cells.
How can mnemonic techniques help with remembering mitosis?
Mnemonic techniques, such as imagery mnemonics, acronyms, acrostics, rhymes, and chunking, can be used to create associations and make the process of memorizing the stages of mitosis easier and more memorable.
Why are mnemonic techniques beneficial for studying?
Research has shown that mnemonic strategies enhance learning, retention, and performance in recall exams. Mnemonic techniques can help students organize and recall information effectively, especially for high-yield topics like mitosis on the MCAT.
What are the different types of mnemonic techniques?
The different types of mnemonic techniques include imagery mnemonics, acronyms and acrostics, rhymes, and chunking. Each type of mnemonic has its own advantages and can be used based on personal preference and the nature of the information being learned.